Implementing multiple nodes pytorch training
Training a model through multiple nodes and mulitple processes
0. Introduction
This blog passage focuses on implementing distributed data parallelism training among multiple nodes and multiple processes. Three methods, torch.distributed.launch, torchrun, and mpirun are covered. Using WandB to monitor the training process is also included.
1. Resources
The model and the dataset are from this blog:
https://leimao.github.io/blog/PyTorch-Distributed-Training
The training process refers to this passage:
https://lambdalabs.com/blog/multi-node-pytorch-distributed-training-guide
https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/examples/tree/main/pytorch/distributed/resnet
2. Training environment
GPU driver: cuda-keyring_1.0-1
Virtual environment: conda 23.5.2
Requirements: python==3.10.2
wandb==0.15.8
tensorboard==2.12.3
tensorboard-data-server==0.7.1
datasets==1.16.1
3. Preparing the model and dataset
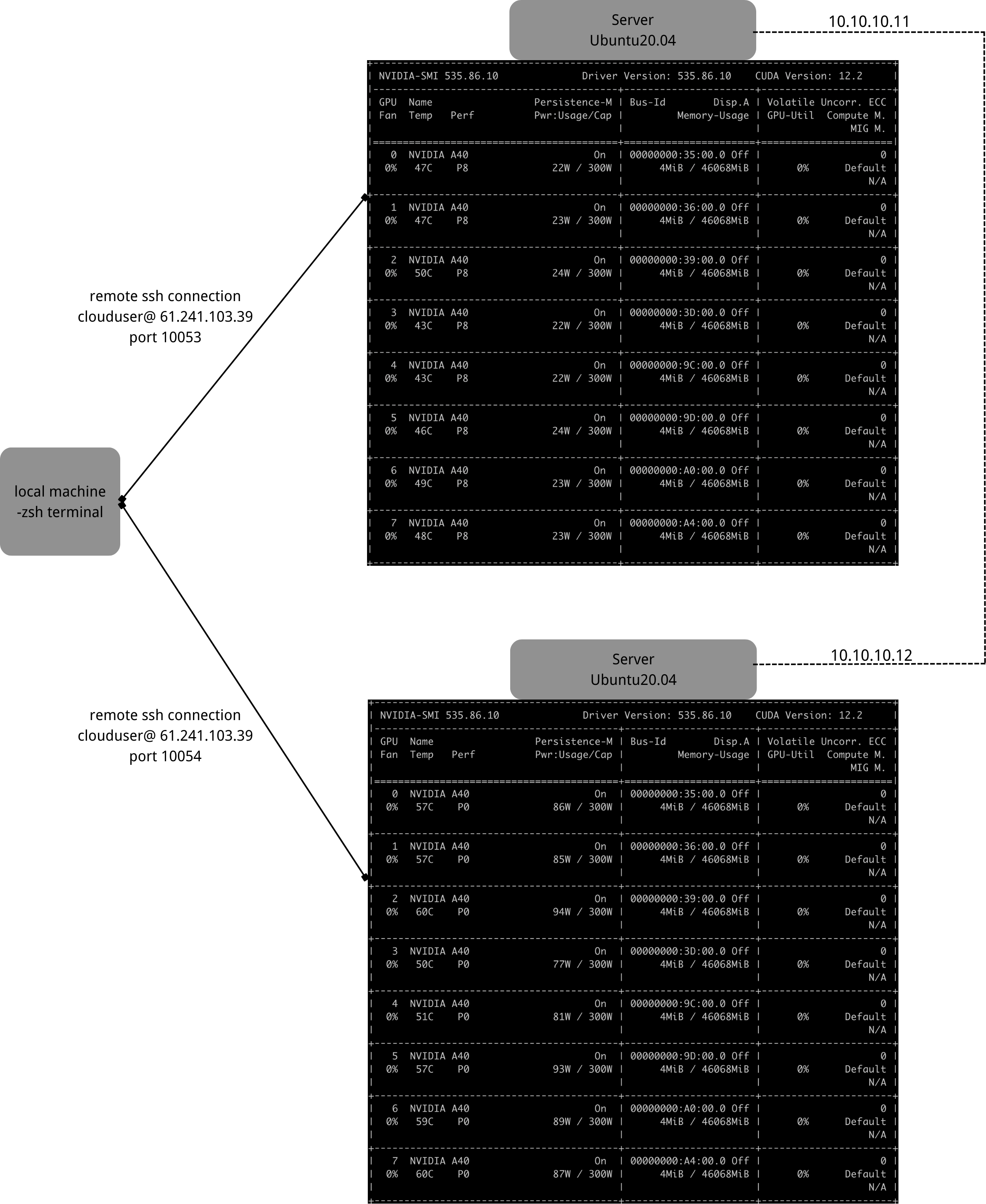
We will deploy the model on two machines as illustrated above, each node is equipped with 8 GPUs. First of all, we have to make sure that the two nodes are connected through ssh. We can set up ip address using the following code on one machine:~$ sudo ip address add 10.10.10.11/24 dev ens11f1
and on the other machine:~$ sudo ip address add 10.10.10.11/24 dev ens11f1
You can use~$ ip a
to check the ip address settings. Then we can use the ssh key to enable ssh connection without a password between the two nodes.
Download the Python script from this repo and the dataset as shown in Mao Lei’s article on each machine.
To view the information during the training process on WandB, we need to add some pieces of code that upload the parameters we want. First, we have to initiate WandB in the code, but only on the main process on the main node:
1 | if (LOCAL_RANK == 0 and WORLD_RANK==0): |
Make sure that WandB is initiated only on the main process in the main node and before enumerating the training epochs. LOCAL_RANK is the rank of the local GPUs, from 0 to 7 on each node. You can specify a random one as the main process. WORLD_RANK is the priority of the machines. The main node is ranked 0. In the code, project=project_name sets the project title displayed on WandB. config argument is optional. We can pass some hyperparameters about the model to it. For more information, check out this document about the .init() function.
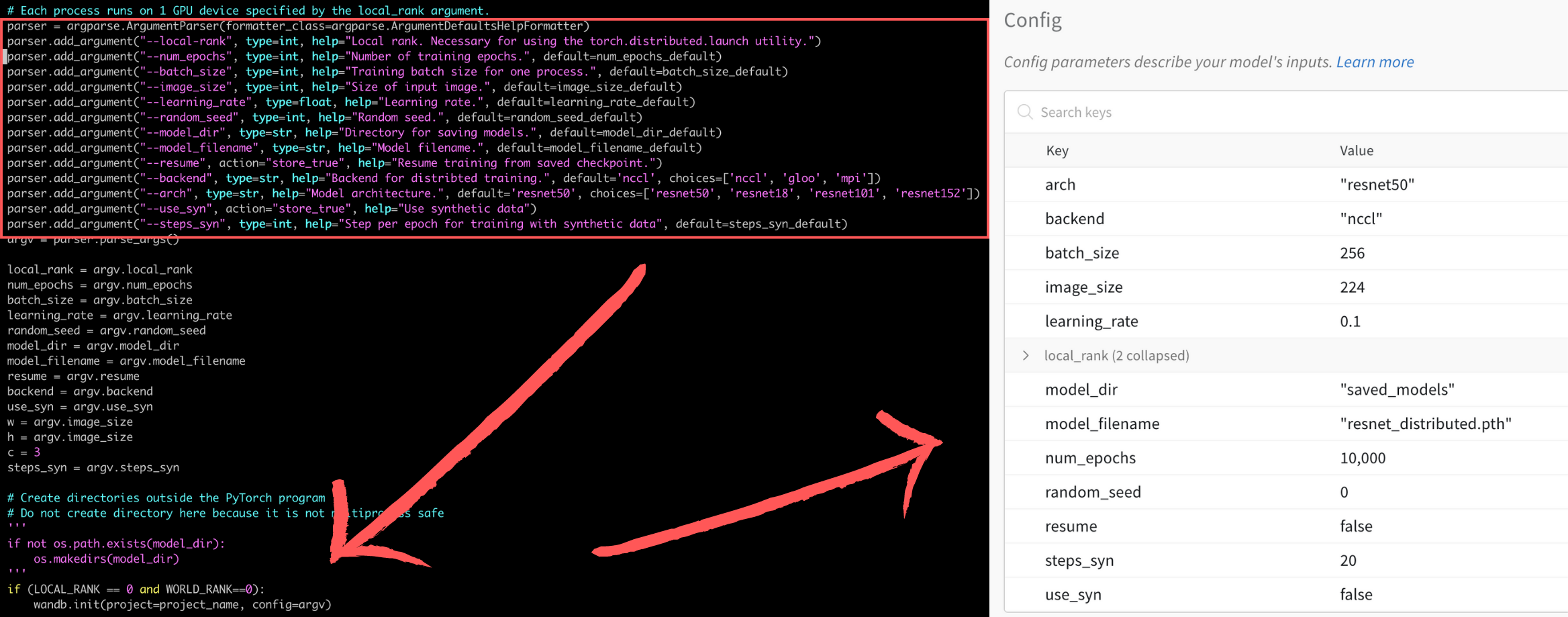
Furthermore, we want to periodically upload parameters like loss rate and accuracy during training, so in the training loop, we can add
1 | if LOCAL_RANK == 0: |
after Line 171 and
1 | if (LOCAL_RANK == 0 and WORLD_RANK==0): |
after Line 201.
The complete code looks like:
1 | import torch |
4. Training the model using Distributed Data Parallelism
In order to use torch.distributed.launch, we need to run the following codes on two machines, respectively
On the main node:python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=10.10.10.11 --master_port=1234 main.py --backend=nccl --use_syn --batch_size=256 --arch=resnet50
On the worker node:python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=1 --master_addr=10.10.10.11 --master_port=1234 main.py --backend=nccl --use_syn --batch_size=256 --arch=resnet50
nproc_per_nod defines the number of workers on each node. It should equal to the number of GPUs on each node. nnodes defines the number of nodes.The only difference should be –node_rank. The argument –use_syn means to use synthesized data, we can delete it if we use the dataset.
Below are some problems you may encounter:
- “main.py: error: unrecognized arguments: –local-rank=7”
The log reports that the arguments for ranking all the local processes are unrecognized. This may be caused by a mistake in the Python script. We can solve this problem by changing “–local_rank” to “–local-rank” in the code “parser.add_argument(“–local_rank”)”.__ - “torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 6.12
GiB (GPU 6; 44.35 GiB total capacity; 7.46 GiB already allocated; 5.80 GiB free; 7.48 GiB reserved in total by PyTorch) If reserved memory is >> allocated memory try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management and PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF” on each GPU.
The error reports that the GPUs run out of memory. First, we may want to check if there are other running processes on the GPUs that occupies the memory.~$ nvidia-smi
If there are irrelevant processses running on the GPUs like above, we can kill the processes by~$ sudo killall python
Or terminate the processes using PID:~$ sudo kill -9 [PID]
Sometimes when the previous attempt to train the model didn’t terminate properly, the terminal would report that the port is already in use when we are trying to start another attempt. In this case we can use~$ sudo netstat -lnput
to check the process that occupies the port and terminate the process.
If the the GPUs still run out of memory even after clearing the processes, we have to consider adjusting the parameters like lowering the batch size and using a smaller model. Adjusting the argument to–batch_size=256, –arch=resnet50will be valid for the A40 GPUs in this case.
Torchrun works similarly to torch.distributed.launch:
master:torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=10.10.10.11 --master_port=1234 main.py --backend=nccl --use_syn --batch_size=256 --arch=resnet50
worker:torchrun --nproc_per_node=8 --nnodes=2 --node_rank=1 --master_addr=10.10.10.11 --master_port=1234 main.py --backend=nccl --use_syn --batch_size=256 --arch=resnet50
Although the above methods work well for DDP on two nodes, they require run command on each node, making it inconvenient when there are more nodes. By contrast, We can launch the DDP training by only typing the command on the master node using mpirun. You can refer to the mpirun section in the passage Multi Node Pytorch Distributed Training Guide for People In a Hurry for installation of OpenMPI and NCCL. Before training, we have to make sure that OpenMPI and NCCL are installed on all of the nodes, and they all use similar virtual environments. To start the DDP training using mpirun, we run the following command on the main node only:mpirun -np 16 -H 10.10.10.11:8,10.10.10.12:8 -x MASTER_ADDR=10.10.10.11 -x MASTER_PORT=1234 -x PATH -bind-to none -map-by slot -mca pml ob1 -mca btl ^openib python3 main.py --backend=nccl --use_syn --batch_size=256 --arch=resnet50
The PATH argument ensures that the script runs in the specified environment.
Implementing multiple nodes pytorch training
http://gong208.github.io/2023/08/19/2023-08-19-multi-nodes-multi-processes/